If you’ve ever had the pleasure of being sucked into an art project, you know how calming and enjoyable it can be. So, it’s probably no surprise to learn that creating art is considered a powerful therapeutic intervention by mental health experts, and one that has been used to treat anxiety, depression and even trauma in children. Let’s take a deep dive into how and why art therapy works to shed some light on this underrated form of mental health therapy.
Art therapy is a therapeutic technique that incorporates methods of creative expression—often through visual media, such as drawing, painting or sculpting—in order to help participants better understand their feelings and behavior. This type of therapy has been used in conjunction with traditional therapies to help treat mental and physical health conditions affecting both children and adults, including everything from stress and anxiety to asthma and cancer.
Though we don’t know exactly why this kind of therapy works, art therapy proponents believe that art can serve as a springboard for awakening memories and rediscovering suppressed thoughts from the unconscious mind. Though the benefits of this type of therapy can be felt in less formal settings, experiencing art therapy in a clinical environment with a professional therapist is recommended. Art therapists have a deep understanding of how specific mediums, textures and colors can affect the process, and they can help those with more severe conditions.
Examples of Art Therapy
There’s no single medium of art that’s best-suited for this type of therapy; however, visual art is the most common method. Some examples of art therapy activities include:
- Drawing, painting or sculpting a self-portrait.
- Creating a painting with a diamond art kit.
- Using crayons or markers to draw emotions.
- Creating a collage to express inner thoughts.
- Drawing or painting the place where you feel safe.
- Keeping a sketchbook to draw thoughts throughout the day.
- Draw yourself in a nature scene.
- Creating paper crafts, such as cards or origami.
- Drawing your feelings after listening to a song or poem.
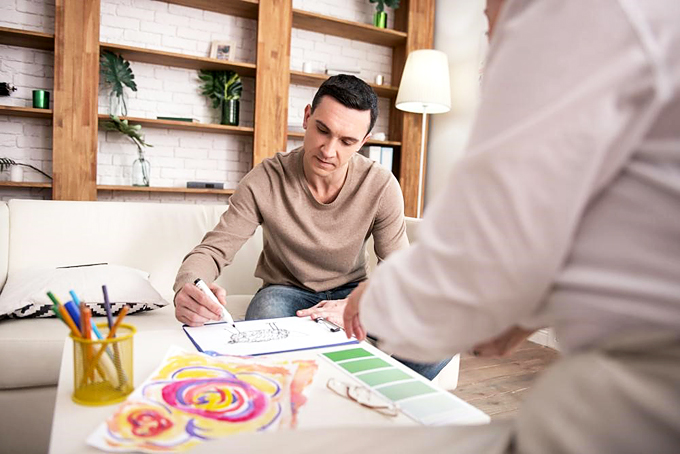

Mental Health Benefits of Art Therapy
According to the American Art Therapy Association, art therapy is used to “improve cognitive and sensory-motor functions, foster self-esteem and self-awareness, cultivate emotional resilience, promote insight, enhance social skills, reduce and resolve conflicts and distress and advance societal and ecological change.” Some of the more well-studied benefits of art therapy include the following.
- It Reduces Stress and Anxiety—There have been a number of studies conducted on the efficacy of art therapy in people with anxiety. One study showed that children with asthma who participated in hour-long art therapy sessions once a week for seven weeks experienced improved feelings of worry, communication, anxiety and self-concept. The therapy has also been used to treat hospitalized children with anxiety as well as prisoners with pre-release anxiety. Making art gives participants a sense of calm, productivity and mindfulness, which can effectively lessen their feelings of stress, worry and anxiety.
- It Reduces Depression—For the same reasons art helps with anxiety, it can also help with depression. The reason why it’s such an effective form of depression therapy is multifaceted, but one of the biggest contributors is that it serves as a non-verbal form of self-expression for people struggling with deep, dark and challenging emotions that are tough to articulate with words. Painting, drawing or completing a relaxing craft can help those with depression and mood disorders feel more comfortable being honest about their feelings, which can lead to more effective therapies and a stronger understanding of the issue.
- It Stimulates Mental Function—If you’re ever feeling dull or like you can’t concentrate, consider breaking out your paintbrush or a set of colored pencils. Studies show that art therapy has the power to increase a participant’s concentration, even in children. Creating art can help you sink into a state of stimulated relaxation, allowing your brain to focus on something without the stress of overthinking. Many forms of creativity can lead to a stronger sense of focus, whether it’s visual art, writing or sewing. You may emerge from the experience feeling a sense of tranquility but also feeling ready to attack a mental challenge.
- It Improves Self-Esteem—An individual’s feelings of self-worth are closely linked to broader and riskier mental health concerns, including depression and suicidal thoughts. Art therapy has been used to improve self-esteem in a variety of different populations, including those particularly vulnerable to low self-esteem. For example, it has been used to improve self-esteem in pre-adolescent girls as well as those in the LGBT community and those struggling with gender identity.
- It Provides a Creative Release—Never underestimate the power of a good, old-fashioned creative release! Creating something beautiful leaves the artist with a strong sense of self-satisfaction, while stimulating the creative side of the brain. The self-satisfaction and tranquility one feels after a period of creative exploration can lead to improved feelings of happiness, confidence and inner peace. Coupled with the benefits of self-expression, this creative release can help participants reach a deep state of joy and understanding during and after their session.

Even Greater Potential
As the mental health field grows and more research is conducted, we expect to see art therapy blossom into the mainstream, with more and more condition-specific treatments developed. Although art therapy is still growing, there is a good amount of evidence suggesting that it has very real and very powerful benefits that should be considered by anyone seeking effective ways to address serious mental health issues.