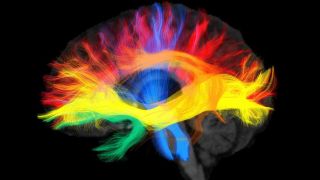
So, what is virtual reality? The aim is to change human perception through a virtual system. Basically, sensory information seems so realistic to the brain being deceived into seeing virtual reality.
Consumer adoption of this technology is still in its infancy but has proved popular in the gaming industry. Now, along with increasing innovation, more and more businesses are identifying ways to use VR as well.
Here are some fields that have benefited from using VR.
Automotive:
Virtual reality in the automotive industry has changed the processes for design, security, and purchasing. Realistic elements of VR allow designers and engineers to check how the car will look and function without having to build several models. Virtual replication of the outside environment also allows for safety testing of vehicles without using the time and energy needed to carry out the actual test.
Major brands such as Ford, Volvo and Hyundai use VR not only for the development process, but also in sales. All vehicle lines are available to customers who can do everything from trying different features to test driving. The needs of dealer showrooms can become obsolete with the use of virtual reality technology.
Health:
Using a realistic virtual environment or virtual model of human anatomy, health care professionals can gain insight into what they will experience before actually working on the real body. This is useful not only for students, but also for experienced professionals who carry out new or high-risk procedures.
Operations can now be viewed from 360 degrees and in real time from around the world with VR applications such as Medical Reality. Not only can surgery be seen with VR, but robotic surgery can now be done with technology.
The opportunity for decentralized patient care is also very useful. The virtual reality application is being designed to learn about patients and examine them in the same way as a health care professional. The time and income saved from these treatments can be significant.
Tourism:
Virtual reality allows for guided tours from anywhere in the world. Nailed to advance the tourism industry, people can now ‘try before they buy’ destinations. This will mainly help smaller and less well-known places, because tourists can observe what each destination has to offer.
Travel and hospitality companies can also display destinations and accommodations. Interactive technology allows prospective hotel or resort guests to explore and experience reasons before ordering. Some companies have gone further to re-create the accommodation environment by using real stimulants (wind, aroma, etc.) on potential clients during virtual experiences.
The collaboration between Thomas Cook and Samsung Gear VR is one example, offering realistic presentations of Thomas Cook locations around the world. The effort resulted in almost £ 12,000 and a 40 percent return on investment in the first three months.
Architecture:
The way architects design buildings is the same way virtual reality has the potential. Architects can experiment with all aspects of buildings such as lighting, materials, and layout, while their customers can take a virtual tour of their new home or building and understand every detail about how it looks and feels.
Builders and contractors have better understanding through design process. Editing designs before and during a building can save a lot of money and reduce communication complications.
Retail:
VR allows retail stores to show off everything from different furniture models to several blouse shades without having a product in place. It also allows customers to test products before buying, which has the added benefit of offering retailers insight into consumer behavior.
Social shopping is a virtual reality method that should emerge in the coming years in the comfort of the consumer’s home. The shopping experience will be tailored to the consumer and will even allow you to try the clothes once the body is scanned.
Additional information and interaction provided to consumers will result in greater satisfaction and overall purchases.
Aerospace:
The aerospace industry is becoming increasingly immersive as virtual reality technology makes every step of the construction and maintenance process a collaborative effort. Interactive features facilitate communication and improve understanding between employees in various departments.
Designers, engineers, and manufacturers are able to create products at a much faster pace through behavioral testing and product visualization. A close relationship between the services is possible thanks to the visualization properties of virtual reality, which helps to better understand all the stages of construction and design. Pilots, ground controllers, service technicians and engineers can also manage products more efficiently with this communication gap.
Education:
Education is a field that is conducive to virtual reality, which allows for the virtual diffusion of more immersive teaching environments.
Google is an example. This is to offer “Google Expeditions” to students and teachers to enable them to perform “virtual immersive journeys”. The application was made available to users in July 2017.
Finance:
Virtual reality has also appeared in the world of finance.
For example, US bank Wells Fargo was one of the first banks to begin testing virtual reality by opening a digital lab to test Facebook’s Oculus Rift headset in 2014. The goal was to enable customers to “virtually
Various banking VR applications have also been launched to offer new digital banking experiences over the years. In June 2017, BNP Paribas launched its virtual reality application, which was deployed to enable retail bank users to access their account activity and transactions in a virtual reality environment.
Manufacturing:
Ford automaker uses VR to design new vehicles, including autonomous vehicles, in its immersion and innovation labs in America since 2015.
In September 2017, Ford also launched a test to begin testing mixed reality for rapid prototyping with Microsoft’s Hololens helmet. Other manufacturers, such as BAE Systems and General Motors, have also begun testing virtual reality.
Marketing:
Marketing may well be one of the first industries to explore virtual reality through campaigns and advertising.
For example, in 2014, Volvo unveiled the “VolvoReality” test of its XC90 SUV, which the company delivered as an application using the Google Cardboard Helmet. Recent projects include Samsung with the release of its VR headsets in some stores to market its products.
Film and entertainment:
Hollywood filmmakers Ridley Scott and Steven Spielberg have been working on projects using virtual reality technology that should revolutionize the way we watch movies. Owners of virtual reality headsets such as Samsung Gear VR also have the option to watch movies in virtual reality.
Source: Benefits of Virtual Reality in Different Businesses Sectors – TechiExpert